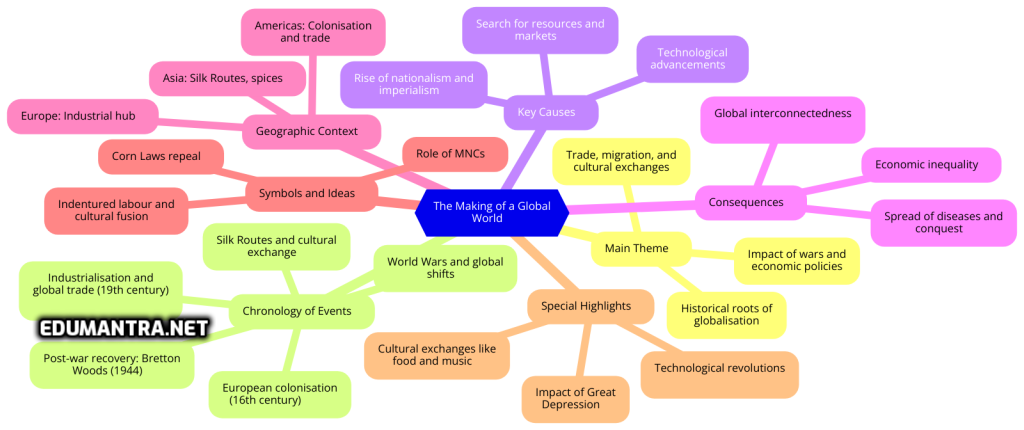
Here is The making of a Global World mind map from your Class 10 Book India and the Contemporary World – II. We’ve made it really very simple to get to know everything about the Chapter The making of a Global World including key events, timelines, causes, consequences, and important figures. Following is the downloadable image file of the Mind Map-
The Making of a Global World: A Simplified Guide
This chapter explains the historical development of globalisation, covering its roots, key events, and the forces that shaped the interconnected world we live in today. It highlights important events, key players, and the outcomes of global interactions.
Introduction to Globalisation
Globalisation is not just a modern phenomenon. Its roots lie in ancient trade routes, cultural exchanges, and migrations. Understanding this history helps us grasp how the world became interconnected.
Also Read:
The Main Theme: Historical Roots of Globalisation
The chapter focuses on how trade, migration, and cultural exchanges built a globally connected world. It explains how wars, industrialisation, and economic policies shaped today’s global economy.
Chronology of Key Events
The Silk Routes: Early Connections
The Silk Routes linked Asia, Europe, and Africa, enabling the exchange of goods like silk and spices, as well as ideas and cultures.
European Colonisation (16th Century)
Europe’s colonisation of the Americas and Asia expanded global trade and introduced new crops, commodities, and systems of labour.
Industrialisation and Global Trade (19th Century)
The Industrial Revolution transformed production and trade, creating a global economy driven by industrial goods and raw materials.
World Wars and Global Shifts
The two World Wars disrupted trade, but they also reshaped political and economic alliances.
Bretton Woods and Post-War Recovery (1944)
The Bretton Woods Conference laid the foundation for global economic stability through institutions like the IMF and World Bank.
Key Causes of Globalisation
Search for Resources and Markets
Nations expanded trade routes and colonies to secure resources and new markets.
Technological Advancements
Inventions like the steam engine, telegraph, and railways made trade and communication faster and cheaper.
Rise of Nationalism and Imperialism
European powers competed for global dominance, pushing colonisation and industrialisation.
Consequences of Globalisation
Spread of Diseases and Conquest
European colonisation brought diseases like smallpox to the Americas, devastating local populations.
Economic Inequality
Colonial systems created wealth for some regions while impoverishing others.
Global Interconnectedness
Cultural exchanges, migrations, and trade fostered mutual dependence among nations.
Geographic Context: Key Regions of Globalisation
Asia
Asia played a major role in trade through the Silk Routes and the export of goods like spices and textiles.
Europe
Europe became the industrial and colonial hub, driving global trade and political control.
Americas
The Americas contributed resources like gold, silver, and new crops, reshaping global trade.
Symbols and Ideas That Shaped the Global World
Multinational Corporations (MNCs)
MNCs emerged as powerful players in global trade and production.
Corn Laws Repeal
The abolition of the Corn Laws in Britain symbolised the move towards free trade.
Indentured Labour and Cultural Fusion
Labour migration from India and China created multicultural societies in colonies like the Caribbean.
Special Highlights: Exam-Relevant Concepts
Technological Revolutions
Inventions like refrigerated ships and assembly lines transformed industries and food trade.
Impact of the Great Depression
The economic crisis of 1929 highlighted the fragility of global trade and finance.
Cultural Exchanges
Foods like potatoes, chillies, and tomatoes changed diets worldwide, while music and art fostered shared cultural identities.
Conclusion: Understanding the Global World
The chapter shows how trade, migration, and technology shaped a globalised world. It helps students understand the connections between historical events and modern globalisation, providing valuable insights for exams and beyond.